- Tel: +86 15759270795
- Email: Sales@touchkey-china.com

Core specialist at Goodkey Machinery with 25+ years in touch springs. Translating complex precision engineering into sharp, expert insights. Mastering the art of the coil.
Capacitive touch buttons are widely used in modern electronic products due to their long lifespan, sealed structure, and flexible design possibilities. From consumer electronics to industrial control systems, capacitive touch technology has gradually replaced traditional mechanical buttons in many applications.
With over 25 years of manufacturing expertise since 2000, we have witnessed the evolution of touch technology from simple tactile switches to the highly sensitive capacitive systems used today. This article integrates our front-line production data and R&D insights to provide a comprehensive engineering perspective. The content is based on practical design experience and real-world applications, making it especially useful for engineers, product developers, and B2B buyers.
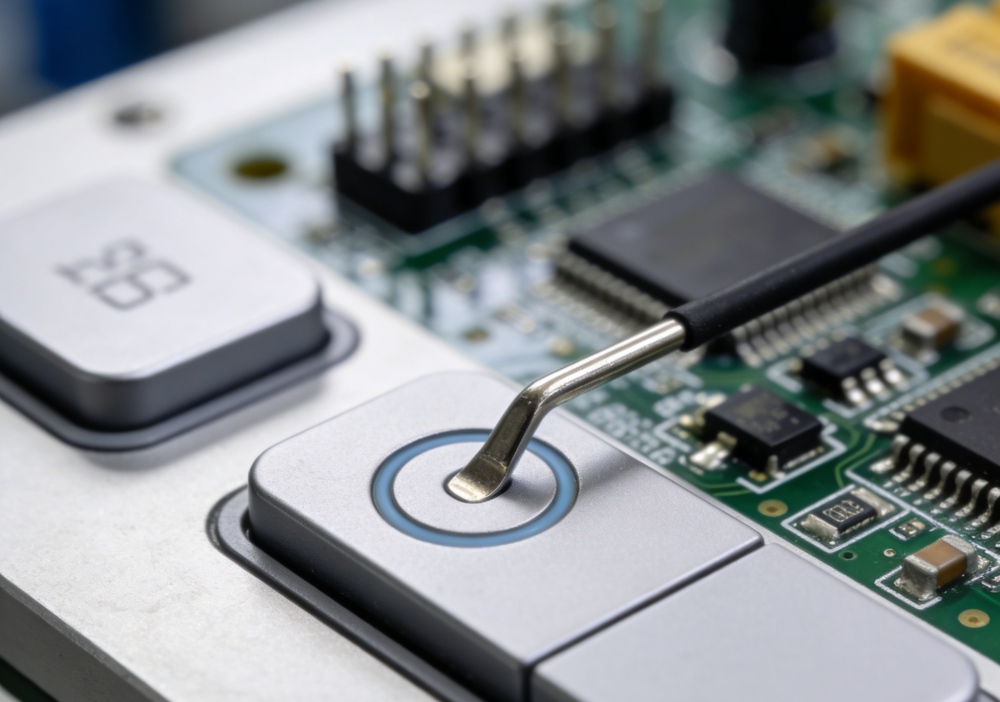
A capacitive touch button is an electronic input device that detects user interaction by sensing changes in electrical capacitance rather than relying on physical movement or pressure.
A typical capacitive touch button system includes:
When a human finger or another conductive object approaches the sensing electrode, it disturbs the local electric field. This disturbance changes the capacitance value of the electrode, which is detected by the control circuit and interpreted as a valid touch input.
Because there are no mechanical moving parts, capacitive touch buttons are considered non-contact input devices, offering higher durability and better environmental resistance than traditional switches.
A capacitive touch key is a specific implementation of capacitive touch technology, commonly used in control panels and user interfaces.
Capacitive touch keys are frequently found in:
Compared with mechanical keys, capacitive touch keys provide a smoother user experience and allow designers to create flat, seamless surfaces that are easier to clean and protect against water and dust.
In high-end applications like those for Electrolux (Germany), the choice of a spring-based capacitive structure is often preferred over simple PCB pads. Our 2008 innovation milestone—the industry’s first compression spring with an integrated metal plate—proved that combining mechanical stability with capacitive sensitivity is the gold standard for premium appliance interfaces.
The working principle of capacitive touch buttons can be explained step by step.
Under normal conditions, a small and stable capacitance exists between the sensing electrode and ground. This baseline capacitance remains relatively constant when no touch is present.
When a finger approaches or touches the sensing area, the human body acts as a conductor and introduces additional capacitance into the system. This newly formed capacitance is effectively connected in parallel with the original electrode-to-ground capacitance.
As a result, the total capacitance increases noticeably.
The capacitive sensing circuit continuously monitors the capacitance value of the electrode. Once the change exceeds a predefined threshold, the system recognizes it as a valid touch event.
The detected signal is amplified, filtered, and processed by a microcontroller or control IC, which then triggers the corresponding function, such as switching, dimming, or mode selection.
This non-contact detection mechanism allows capacitive touch buttons to offer fast response times, high sensitivity, and consistent performance.
From both a product design and engineering perspective, capacitive touch buttons offer several advantages.
Capacitive buttons respond to light touch without requiring physical force, reducing user fatigue and improving usability.
Because there is no mechanical wear or friction, capacitive touch buttons can operate reliably for millions of cycles.
The absence of mechanical gaps enables fully sealed designs, making capacitive buttons suitable for waterproof and dust-proof applications.
Capacitive touch buttons support various shapes, materials, and backlighting designs, giving industrial designers more creative freedom.
Despite their advantages, capacitive touch buttons also present certain challenges that must be considered during design.
High humidity, water droplets, or electromagnetic interference may affect detection accuracy.
Thick gloves or insulating materials can reduce sensitivity if not properly designed.
Poor grounding, routing, or electrode design can cause false triggering or instability.
In real-world applications, these issues are usually addressed through proper electrode geometry, shielding, grounding strategies, and sensitivity calibration.
Understanding the differences between capacitive and mechanical buttons helps in selecting the right solution.
Mechanical buttons rely on physical movement and contact, which can wear out over time. They also require openings in the housing, increasing the risk of water and dust ingress.
Capacitive touch buttons, on the other hand, offer:
However, mechanical buttons may still be preferred in applications requiring tactile feedback or operation with heavy gloves, highlighting the importance of application-specific design choices.
Capacitive touch technology is widely used across multiple industries.
Smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices rely heavily on capacitive touch interfaces for intuitive interaction.
Capacitive touch buttons are used in automation equipment and control terminals where durability and ease of cleaning are critical.
Medical equipment benefits from sealed capacitive interfaces that support frequent cleaning and disinfection.
Capacitive touch controls are increasingly used in dashboards, infotainment systems, and steering wheel interfaces.
From years of experience in capacitive touch component design and manufacturing, it is clear that stable performance depends on more than just the sensing IC.
Key factors include:
Successful capacitive touch solutions result from a balanced combination of electrical engineering, mechanical design, and real-world testing—especially in B2B and industrial environments.
Q1: Can capacitive touch buttons be operated with gloves?
A: Yes. However, optimal performance requires precise sensitivity tuning. Depending on the thickness and material of the gloves, electrode design may need specific adjustments to ensure reliable triggering and responsiveness.
Q2: Are capacitive touch solutions reliable for rigorous industrial environments?
A: Absolutely. When engineered with precision, capacitive touch interfaces offer exceptional reliability and long-term stability. By utilizing high-quality materials and professional design, they withstand the challenging conditions typical of industrial applications.
Q3: What is the expected lifespan of capacitive touch buttons?
A: Capacitive touch components significantly outlast traditional mechanical switches. Because they operate without moving parts, there is no mechanical wear and tear, ensuring a much longer service life and sustained performance over time.
Capacitive touch buttons have become a key input solution in modern electronics thanks to their durability, design flexibility, and user-friendly operation.
For engineers and product developers, understanding how capacitive touch buttons work and how to design them properly is essential for achieving stable, reliable performance in real-world applications.
When implemented with the right engineering considerations, capacitive touch technology offers a powerful alternative to traditional mechanical input solutions.
Leave A Message
Scan to Wechat/Whatsapp :

